
With increasing statistics on GRBs, a new study now confirms a 50% likelihood of a devastating GRB event on Earth in the past 500 Myr.
Some scientists have proposed that a GRB could have been at the origin of the Ordovician extinction some 450 Myr ago, which wiped out 80% of the species on Earth. This would be enough to cause a massive life-extinction event.
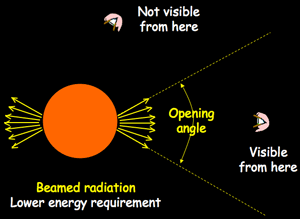
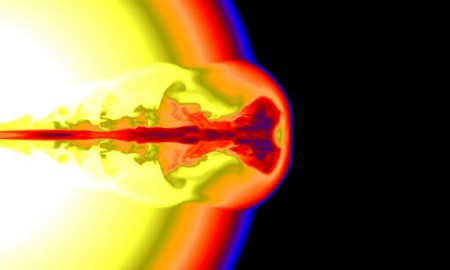
Calculations suggest that a fluence of 100 kJ/m 2 would create a depletion of 91% of this life-protecting layer on a timescale of a month, via a chain of chemical reactions in the atmosphere. If one were to happen nearby, the intense flash of gamma rays illuminating the Earth for tens of seconds could severely damage the thin ozone layer that absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. The luminosity of long GRBs – the most powerful ones – is so intense that they are observed throughout the universe ( CERN Courier April 2009 p12). If such a jet is pointing towards Earth, its high-energy emission appears as a GRB. If this process leads to the formation of a rapidly spinning black hole, accreted matter can be funnelled into a pair of powerful relativistic jets that drill their way through the outer layers of the dying star.

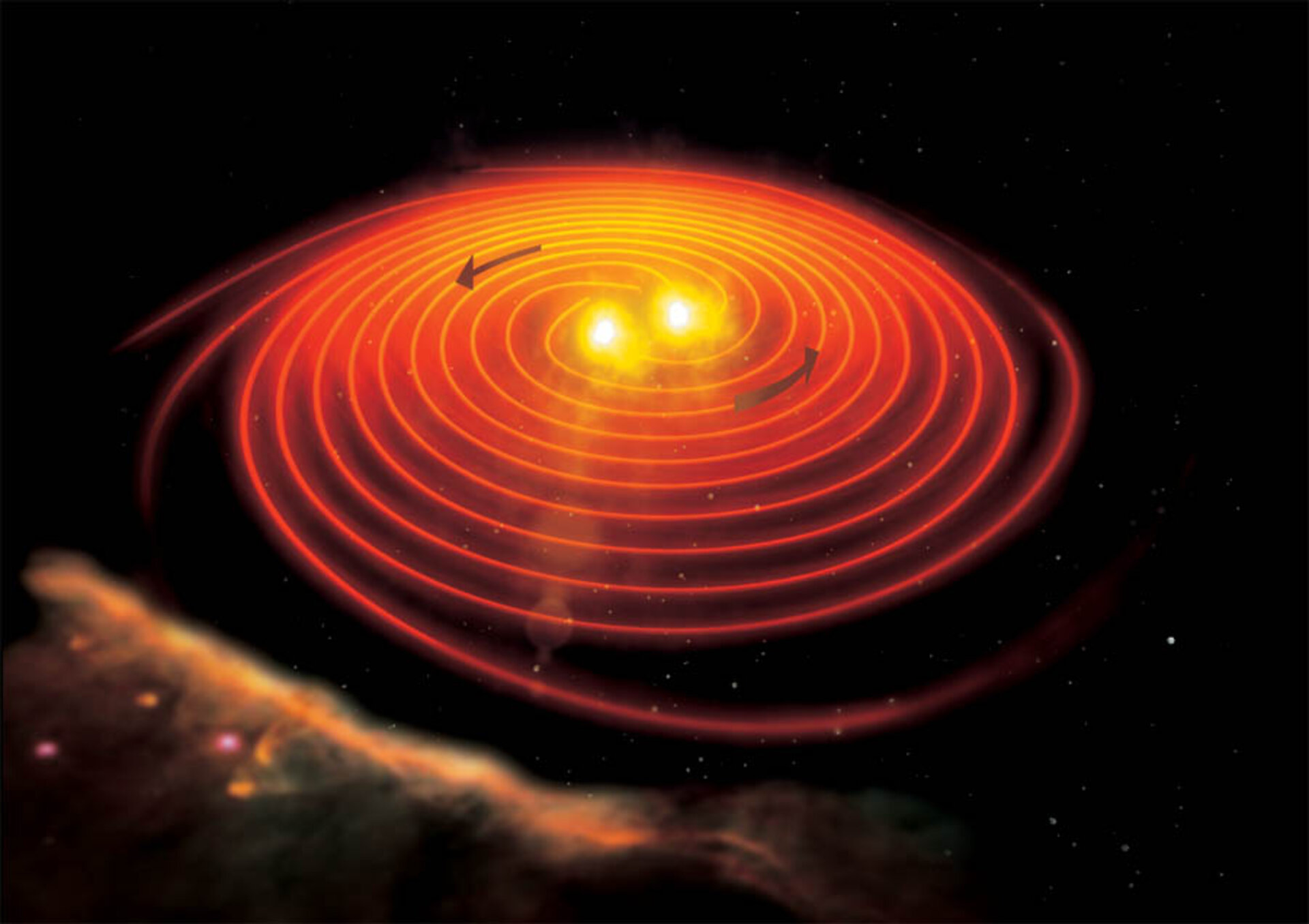
When nuclear fuel is exhausted at the centre of a massive star, thermal pressure can no longer sustain gravity and the core collapses on itself. Their origin remained a mystery until about a decade ago, when it became clear that at least some long GRBs are associated with supernova explosions ( CERN Courier September 2003 p15). GRBs occur about once a day from random directions in the sky. They further estimate that GRBs prevent complex life like that on Earth in 90% of the galaxies. The authors find a 50% chance that a nearby GRB powerful enough to cause a major life extinction on the planet took place during the past 500 million years (Myr). Artist’s rendering of a GRB, where life-damaging gamma rays are produced by two relativistic jets powered by a new-born black hole at the heart of an exploding massive star.Ī new study confirms the potential hazard of nearby gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), and quantifies the probability of an event on Earth and more generally in the Milky Way and other galaxies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
